Take back control of access management with an integrated platform for web, mobile, and cloud
Many organizations face access management chaos. As applications and resources have spread across on premise data-centers and multiple cloud providers, users are often accessing these resources from anywhere and on multiple devices. These simultaneous trends have left access management systems fragmented and access polices inconsistent, resulting in an environment that is expensive to maintain and challenging to secure.
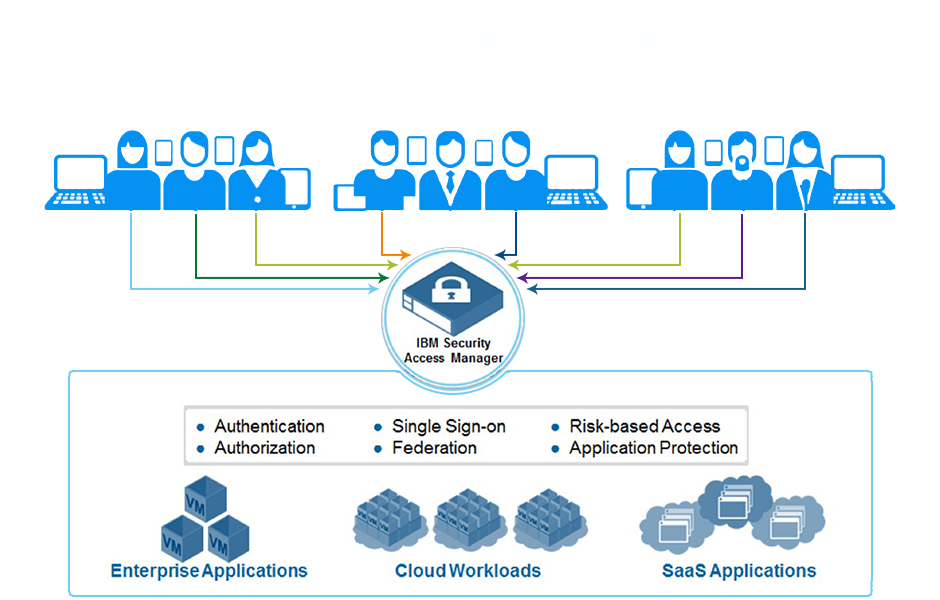
IBM Security Access Manager allows organization to take back control of their access management system with a single integrated platform that manages access across many common scenarios. Access Manager helps secure access points into the corporate network and enforce risk-based access policies that define who and what can access protected resources.
The solution is a modular platform for web access management, web application protection, mobile access management, cloud access management, risk-based access, and identity federation. The integrated appliance form factor allows for easy and flexible deployment and maintenance.
Access Manager helps centrally secure internal and external user access points into the corporate network from web and mobile channels. Highly scalable and configurable, the solution is designed to provide a policy-based user authentication and authorization system that helps defend against the latest web-based security threats.
IBM Security Access Manager delivers a security appliance that helps secure user access and protect content against common web attacks
- Enhanced user productivity while ensuring secure user access to web and mobile applications through single sign-on (SSO), session management, strong authentication, and context-based access policy enforcement.
- Federated single sign-on (SSO), which helps enhance user productivity and facilitates trust through the delivery of SSO across separately managed domains, including easily configurable connections to popular software as a service (SaaS) applications.
- Integration with IBM MobileFirst Platform, IBM MobileFirst Protect (formerly, MaaS360 by Fiberlink, an IBM company) IBM Security Trusteer Fraud Protection for easier mobile access development and rich mobile context for access decisions.
- Better protection from advanced threats including OWASP top 10 web application risks.
One platform offering, with easily consumable add-on Modules
IBM Security Access Manager is a modular, integrated access management appliance that helps secure access to web, mobile, and cloud workloads. The integrated appliance form factor allows for easier and more flexible deployment and maintenance. It is offered both as a physical appliance and as a virtual appliance image that runs on a number of popular hypervisors.
According to the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) top 10 list of web vulnerabilities, external hackers use SQL injections, broken authentication, and cross-site scripting (XSS) as common methods to gain unauthorized access into the web applications. By utilizing research from the IBM X-Force threat research team, Access Manager delivers the ability to help block OWASP top 10 web vulnerabilities before they reach the targeted application.
According to the IBM X-Force Security and Risk trend report, attackers use phishing attacks and social engineering to compromise end-user access to gain unauthorized access into corporate applications. Identity fraud and Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) are growing concerns for enterprises, as they expand their web application reach into mobile, business partner, and social collaborations.
In the face of these challenges, it is important to bring increased intelligence to authentication and authorization. The Advanced Access Control Module allows Access Manager to use detailed contextual information (for example, geographic location, device fingerprint, browser type, application data, and so forth) about the user making the access request when making access decisions
Advanced Access Control key capabilities
- Risk scoring engine to enforce context-aware authorization using information about the users, their mobile devices, and other transactions-based information.
- Mobile sign-on, session management, and an authentication service for supporting multiple strong authentication schemes, for example, one-time password, and Short Message Service (SMS) verification codes.
- Helps provide more secure mobile transactions with a graded level of trust to allow and deny access using mobile device fingerprinting, geographic location awareness, and IP reputation.
- Integration with the IBM Mobile First Platform and IBM Mobile First Protect (formerly, MaaS360 by Fiber link, an IBM company) lets mobile application developers easily incorporate access security.
- Integration with IBM Security Trusteer Fraud Protection lets Access Manager use device fraud and malware indicators in access decisions.
- Provides a graphical policy management interface that supports authoring complex policies.
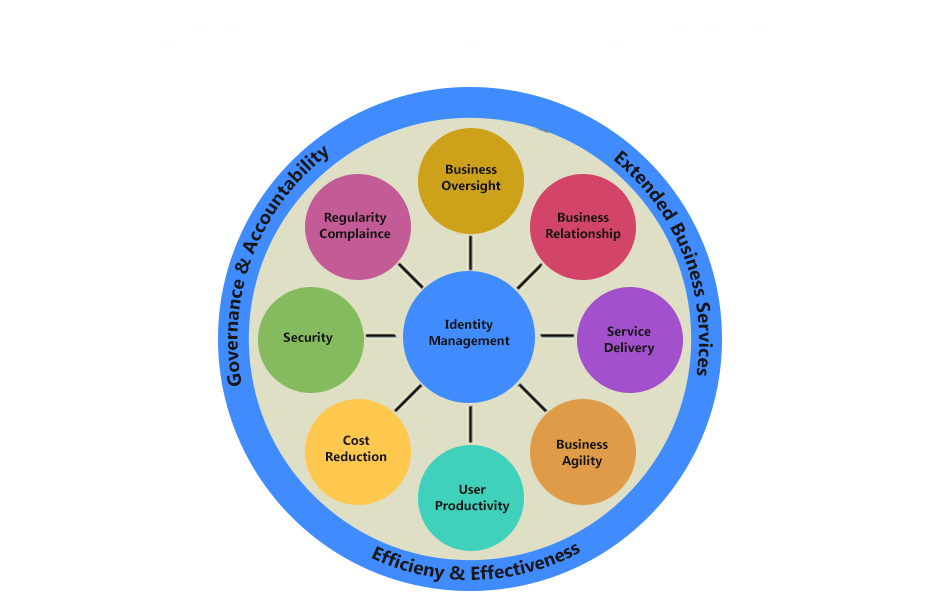
Value from Identity Governance
Good identity governance adds business value and reduces costs in a number of different ways. It focuses effort on business objectives; it improves understanding and helps to facilitate communication between the different parts of an organization. It saves costs through ensuring that solutions meet business needs and through streamlining and automating processes.
It reduces risk through better controls and monitoring to avoid theft, fraud, and misuse of information. It helps to protect the organization against cyber-crime through a better understanding of legitimate activities. It provides a practical and effective approach to compliance. It improves risk management by providing a way to measure how the implementation of policies and controls improves risk over time.
Identity governance facilitates communication between the organization’s board of directors, lines of business, IT security, and IT service providers. The organizational board sets the overall priorities for governance and compliance and these, in turn, set the primary objectives for the control of access. The line of business managers set the objectives for specific systems and understand the sensitivity and value of the data these systems contain. Thus, they have a key input into the requirements to control access to that data. Neither of the previous objectives are technical, nor are the people setting them technicians. These objectives need to be translated into a technical specification and implementation by IT services and IT security staff. Identity governance ensures that the technical architecture and components can be related back to the business requirement and so their need and priority can be understood by all the stakeholders.
Identity governance ensures that the processes and technologies to manage identity and access are focused and built based on real business need. This helps to accelerate the delivery of IT systems and to reduce their cost. By focusing on the real business needs rather than the latest technology it ensures that the IT systems are scoped correctly, built using appropriate technology, and implement the appropriate controls; and as a consequence, helps to avoid function creep in identity projects.